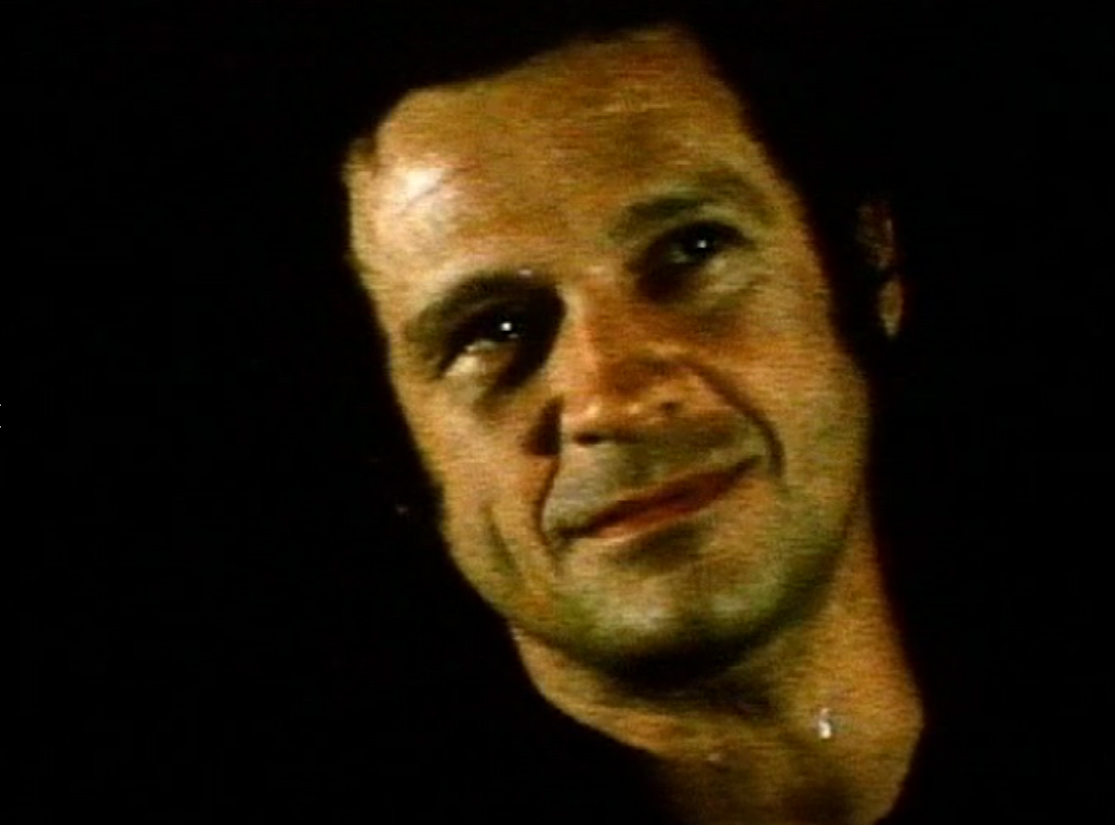
Jack Deveau:
[Credits include Left-Handed, Drive, Ballet Down the Highway, Good Hot Stuff, Wanted: Billy the Kid, A Night at the Adonis, Rough Trades, Sex Magic, Fire Island Fever, Dune Buddies, Times Square Strip]
"We were looking for a while to describe the porno movie because it doesn't really relate to anything else. it is only starting to find its milieu, or genre, whatever you want to call it. It's a musical comedy, but now instead of singing, they fuck. Now that I've been able to make that generalization I think, well, are they going to sing a happy song now or a sad one? What condition is this character in? And then we try to structure the sex in those terms... Good or bad, gay or straight, this is becoming a literature that you can't ignore. Now there are 40 films in our library and there are a number of other organizations or companies who have the same thing. There are magazines in Europe who are devoting whole issues every other month to critiques of the erotic cinema. Eventually this will have to become a literature." -- Soho Weekly News, 1975
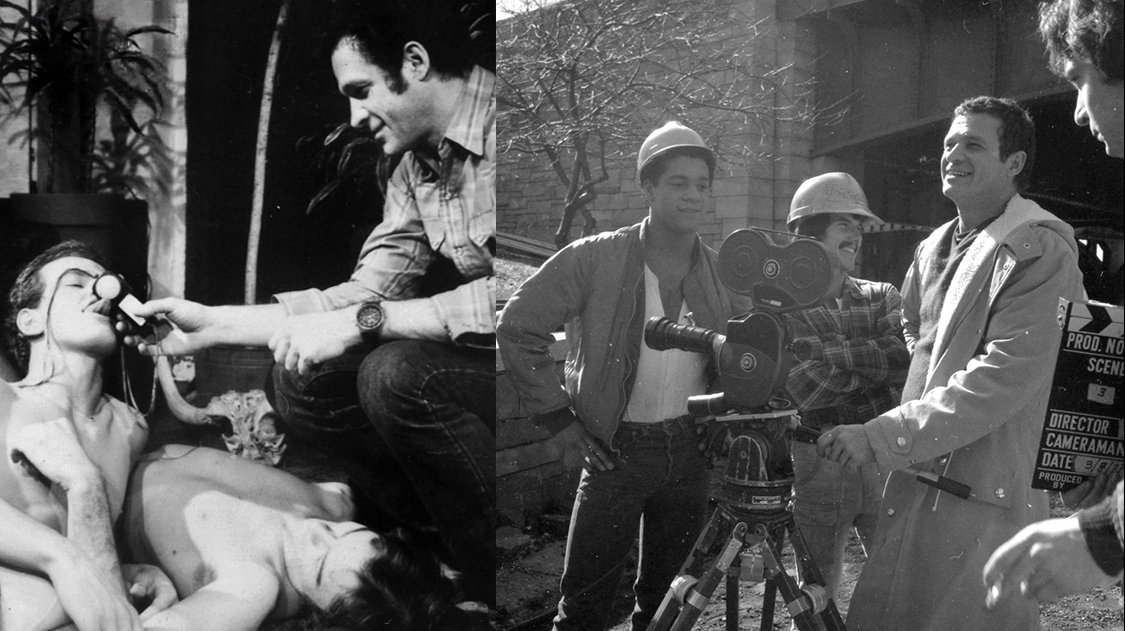


[Credits include The Erotic Films of Peter de Rome, Adam and Yves, The Destroying Angel]
"I think that we've barely scratched the surface of pornography in filmmaking, and that it has become a sort of mandatory thing in sex films to show a positive view of sex and all of the sex is supposed to be the ultimate, the pinnacle of excitement and life simply isn't like that. It seems to me that sometime we've got to get honest about sex and admit to ourselves that very few sexual encounters do work out agreeably or are compltetely successful. I think we can learn from our failures as from our successes. I have a very simple if not simplistic attitude toward sex films, and that is that sex is just as much a part of life as living, eating, breathing, sleeping. It's just another function of life and I don't see why it can't be depicted dramatically just as those other functions are and as honestly, too. And I think we have to show every aspect of sex in films before we can really say we are making sex films."


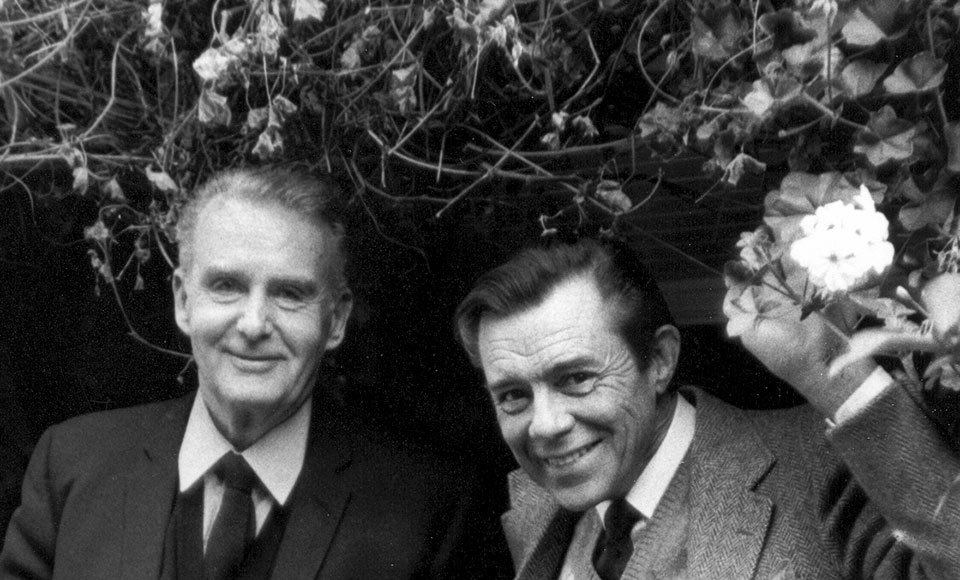
Peter de Rome directing the stars of The Destroying Angel
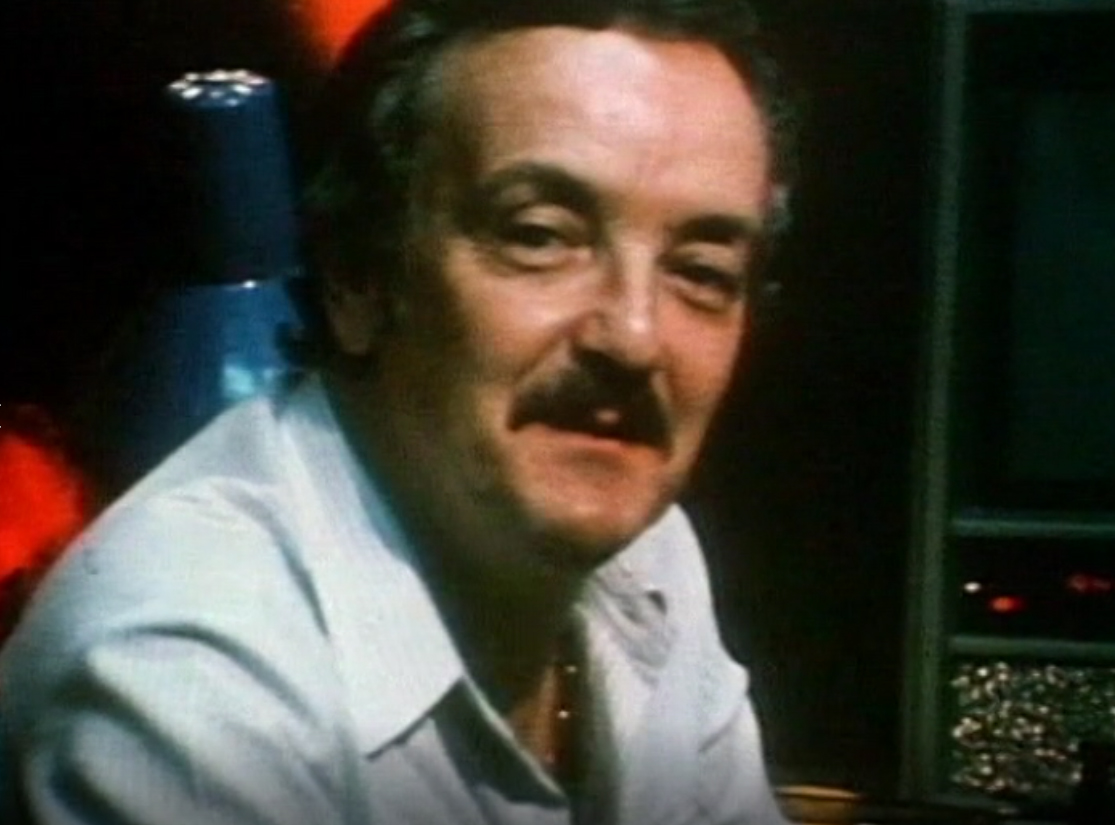
[Credits include The Goodjac Chronicles, Goodjac Too]
"Filmmakers have prettied-up and candy-coated male sex so much that most people who do get off on it don't think that they're worthy of being photographed or seen. That's a real putdown of the community. I don't think it was planned that way, but everybody just got on the bandwagon. Good-looking sex and tantric moments are going on with people who have pot bellies, have hair in the wrong places, or don't have hair in the right places. I believe people want to see that kind of good sex... I'm stepping into this the way those people stepped into those rockets: they believed in what they were doing, they believed it was for a good cause, they believed it would do some good for people, and they just stepped in and did it." -- Mandate, 1986

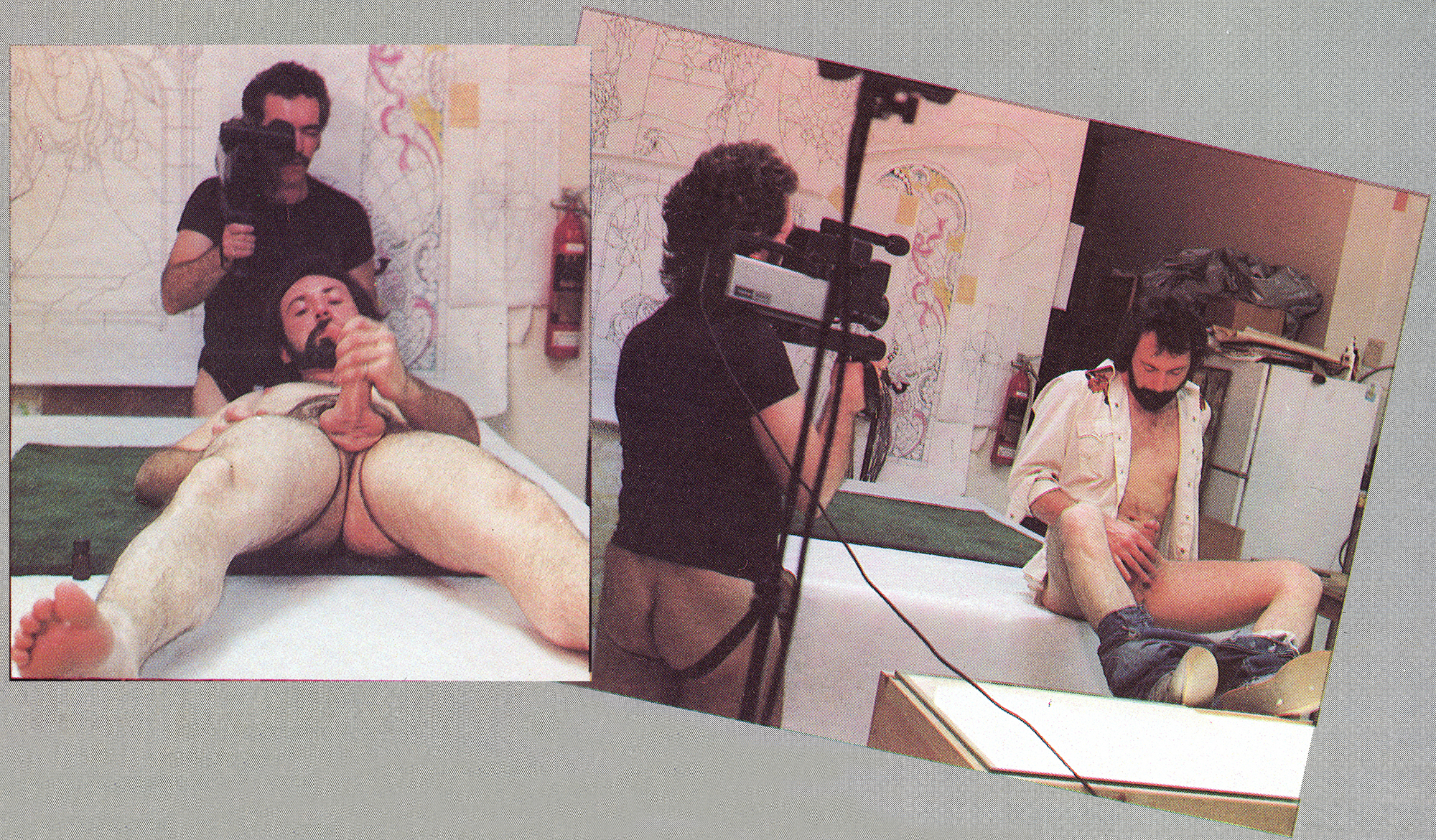
[Credits include Dangerous, Therapy, Head Trips, One in a Billion, Rangers, Oversize Load, Strange Places Strange Things, High Tech]
"Surge is a small company - very small. People are amazed when they find out that Surge was basically two people, my lover, Steven [Steve Taylor], and me. When you think of a studio, you think of M-G-M or Warners, but all of our sets were built in our living room in the house at Hermosa Beach, which was a 1500 square foot house that had a wonderful cathedral ceiling. But if you pulled up my carpets, my floors were ruined. I mean, there were nail holes everywhere. We trashed that house - but that house was our studio. And all of our successful films from One in a Billion to High Tech were done in that house." -- Manshots, 1990

[Credits include Track Meet, Rough Cut, Twelve at Noon, Gemini, Inches, Wanted, Games, Turned On!, A Few Good Men, Screenplay, Non-Stop]
"We're trying to create an erection. Now, to me, that's a feat in itself. It's a harder job than legit films. A lot of people may talk down porno, but I'll stand up to David Lean, to all of 'em, because what we do, in the limited time we do it in... Why, we're now doing 70 to 75 minutes on Inches for maybe ten, twelve thousand dollars. That's unheard of! That's lunch! So, it's an undertaking, and what we've done to date we're proud of, and hopefully we'll go on making milestones. And we don't like to cheat the audience. At least when they come out of the theatre from watching one of our films they're satisfied, they're entertained, and they don't feel like they're ripped off... and they may come back to see the next one." -- Skin, 1980

















 Join our Email List
Join our Email List Like Us on Facebook
Like Us on Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube Follow Us on Twitter
Follow Us on Twitter Follow us on Pinterest
Follow us on Pinterest